Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that primarily affects infants and children under the age of five. However, it can sometimes affect adults too. The disease is characterized by sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet. It is highly contagious and can spread rapidly in communal environments like schools and daycares.
Key Takeaways
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a contagious viral infection common in children.
- Symptoms include fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth.
- The disease is usually mild and resolves on its own, but maintaining good hygiene can help prevent its spread.
- There is no specific treatment for HFMD, but symptoms can be managed with over-the-counter medications.
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by viruses from the Enterovirus genus, most commonly the coxsackievirus. It is distinct from foot-and-mouth disease, which affects livestock. HFMD is recognizable by its unique symptoms, including fever, mouth sores, and a rash with blisters.

Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
The symptoms of HFMD usually appear three to six days after exposure to the virus. This period is known as the incubation period. The initial symptoms often include:
- Fever
- Reduced appetite
- Sore throat
- Feeling unwell
Within a couple of days, painful sores can develop in the mouth. A rash, which may blister, can appear on the hands, feet, and sometimes the buttocks and legs. The rash is not usually itchy, but it can be uncomfortable.
How is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Spread?

HFMD spreads through close personal contact, respiratory droplets from coughs or sneezes, contact with feces, and touching objects or surfaces that have the virus on them. It is most contagious during the first week of illness but can spread for weeks after symptoms resolve.
Causes and Risk Factors
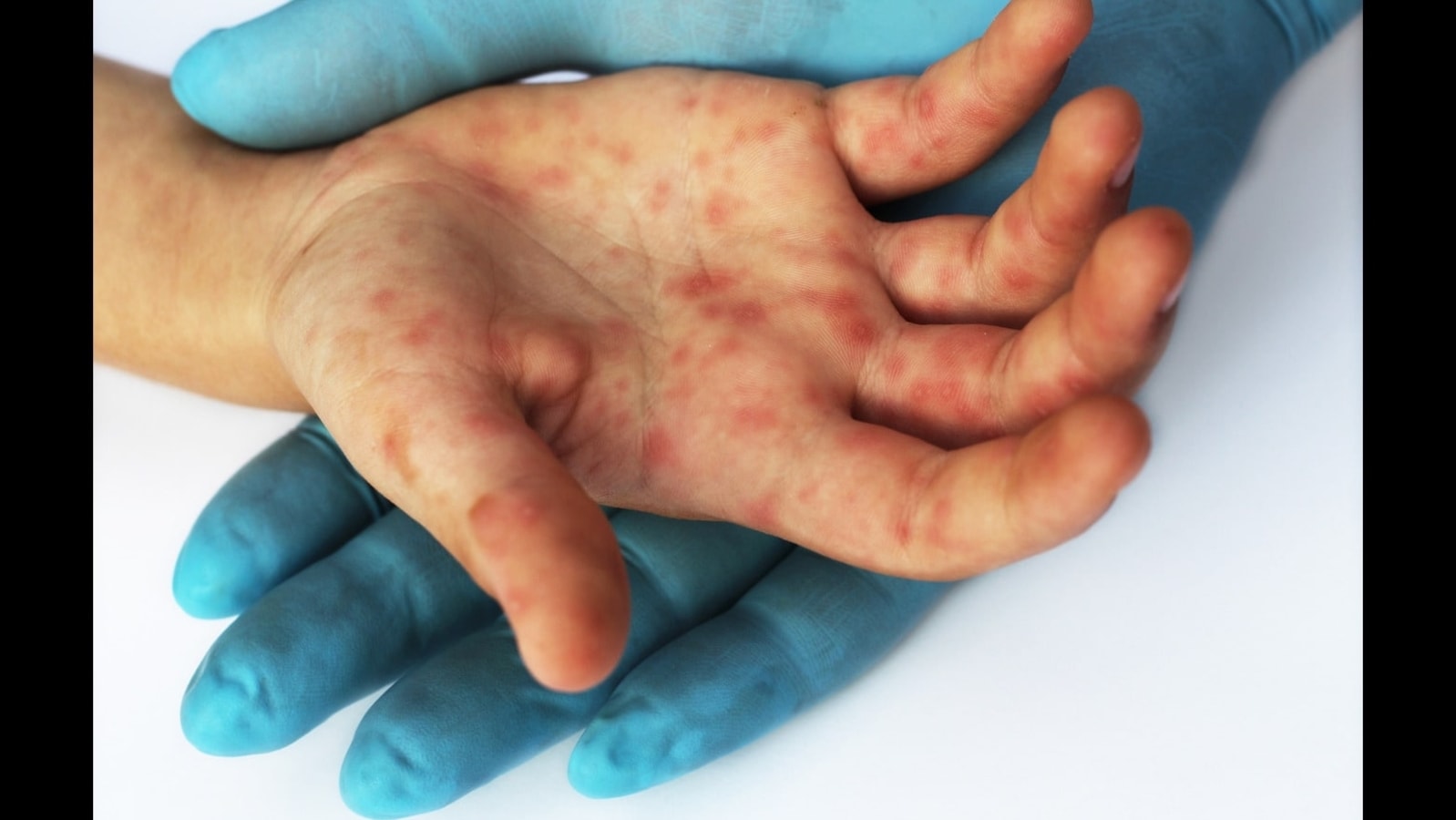
The primary cause of HFMD is the coxsackievirus A16, although other strains of the enterovirus can also lead to the disease. Risk factors include:
- Age: Children under five are most susceptible.
- Close Contact: Being in close quarters with infected individuals, such as in schools or daycare centers.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are at higher risk.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Doctors typically diagnose HFMD based on the signs and symptoms. In some cases, a throat swab or stool sample may be tested to confirm the presence of the virus. There is no specific treatment for HFMD. Most cases resolve without medical intervention. However, symptom relief is possible through:
- Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Topical oral anesthetics to relieve mouth sore pain
- Staying hydrated to prevent dehydration
Prevention Tips
Preventing the spread of HFMD involves good hygiene practices. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of infection:
- Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially after changing diapers or using the toilet.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces and objects, such as toys and doorknobs.
- Avoid close contact, like kissing or hugging, with infected individuals.
- Teach children about the importance of not touching their eyes, nose, or mouth.
When to See a Doctor
While HFMD is generally mild, complications can occur. Seek medical advice if:
- The child is unable to drink enough fluids.
- Symptoms worsen or do not improve after a few days.
- There are signs of dehydration, such as a dry mouth or reduced urine output.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common and typically mild illness that can be managed with proper care and hygiene. Understanding the symptoms and preventive measures can help reduce the spread of the virus. While the disease usually resolves on its own, staying vigilant and consulting a healthcare provider when necessary ensures the well-being of those affected.
By taking simple precautions and maintaining good hygiene, the impact of HFMD can be minimized, keeping children and communities healthy and safe from this contagious virus.…
Read More